Introduction: A Growing Crisis for Europe
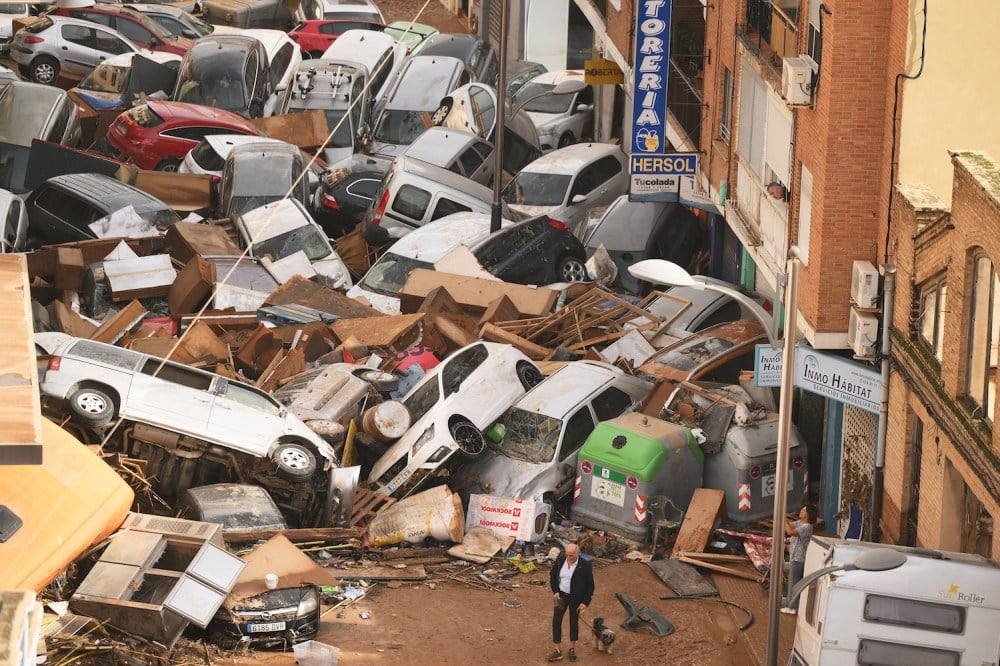
As climate change accelerates, Europe is witnessing an alarming rise in the frequency and intensity of severe flooding. Once considered rare and isolated events, devastating floods are now becoming a recurrent threat to millions of people, with far-reaching consequences for ecosystems, infrastructure, and economies. From catastrophic events in central and southern Europe to the constant threat along the coasts, the continent’s ability to adapt and respond to this new normal will determine the future of its communities and way of life.
This article explores the innovative strategies, cutting-edge technologies, and community-driven responses that highlight Europe’s resilience in the face of increasingly severe flooding. By understanding the causes, effects, and solutions to this escalating threat, we can gain insight into how Europe is confronting its flood crisis—and what more needs to be done.
The Rising Tide: Causes and Impacts of Severe Flooding in Europe
Severe flooding in Europe is not a new phenomenon, but the increasing scale and frequency of these events are largely attributed to the impacts of climate change. Several factors contribute to the intensification of flooding across the continent:
- Rising Temperatures: Higher average temperatures have resulted in more intense rainfall, leading to rapid runoff and overwhelmed drainage systems.
- Sea Level Rise: Coastal areas are experiencing a gradual increase in sea levels, amplifying the risk of storm surges and coastal flooding.
- Melting Glaciers: In regions such as the Alps, the accelerated melting of glaciers contributes to higher river levels and increased flood risks downstream.
- Land Use Changes: Urbanization and the destruction of natural wetlands reduce the land’s capacity to absorb water, exacerbating the effects of flooding.
The impacts of severe flooding are devastating and wide-ranging. Communities in countries like Germany, Belgium, and Italy have faced immense challenges in recovering from massive floods. Lives have been lost, homes destroyed, agricultural lands submerged, and economies severely disrupted. Flooding also exacerbates long-term problems such as water contamination, displacement, and the spread of diseases.
Innovative Flood Management Strategies
In response to this growing threat, European nations have adopted a variety of innovative flood management strategies aimed at both reducing the risk of floods and mitigating their impacts. These strategies combine technology, policy, and community-driven approaches to build resilience across the continent. Some of the most notable strategies include:
1. Smart Infrastructure and Technology
One of the most promising innovations in flood management is the use of technology to predict, monitor, and respond to flood risks. Several cities are deploying advanced flood warning systems that use real-time data to forecast potential flooding events with greater accuracy. These systems rely on weather satellites, river gauges, and AI-driven algorithms to predict when and where floods might occur.
- Flood Barriers and Dams: Modern flood barriers are being constructed using adaptive designs that can respond to fluctuating water levels. In the Netherlands, for example, the Maasvlakte 2 project has created an artificial extension to the Port of Rotterdam, which includes flood-proof infrastructure.
- Smart Drainage Systems: Cities like Paris and Copenhagen have implemented smart drainage systems equipped with sensors that monitor water flow and automatically adjust to prevent flooding during heavy rainfall.
- Flood Prediction Models: European researchers are using machine learning to improve flood prediction models. By analyzing historical weather patterns and river flow data, these models can predict potential flooding hotspots weeks in advance.
2. Nature-Based Solutions
In addition to high-tech solutions, many European countries are turning to nature-based solutions (NbS) to address flooding. These solutions work with natural processes to restore ecosystems and mitigate flood risks. Some examples include:
- Wetland Restoration: Wetlands act as natural sponges, absorbing excess water during heavy rains. In the UK, for example, projects are underway to restore wetland areas, which can help reduce the frequency and severity of floods.
- Riverbanks and Floodplains: The re-establishment of natural floodplains along major rivers like the Rhine and Danube can help dissipate floodwaters before they reach urban areas. In France, the “Living River” project aims to return rivers to their natural course.
- Green Roofs and Urban Greening: In cities like Berlin and Barcelona, urban greening initiatives such as green roofs, permeable pavements, and urban forests have been implemented to increase the absorption of rainwater and reduce the risk of urban flooding.
3. Community-Centric Approaches
One of the key elements of Europe’s resilience to flooding is the involvement of local communities in flood management. These community-centric approaches not only empower citizens but also foster greater awareness and preparedness for flood events. For instance:
- Flood Resilience Training: In the Netherlands, communities have long been involved in flood defense initiatives, with local citizens participating in flood response drills and learning how to use emergency flood barriers.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: The European Union funds public education campaigns to inform citizens about flood risks and the importance of personal preparedness. Such programs have proven effective in minimizing the loss of life and property damage.
- Community-Based Flood Management Plans: In rural areas, local governments are working directly with communities to develop flood management plans that address specific regional needs and vulnerabilities.
The Role of European Policy and Funding
European policy plays a crucial role in coordinating flood management efforts across the continent. The European Union’s Floods Directive, for example, requires all member states to assess flood risks and develop flood risk management plans. These plans must address both prevention and preparedness, with a strong emphasis on public participation and environmental protection.
Additionally, the EU has committed substantial financial resources to support flood resilience projects through programs like the EU Solidarity Fund and Horizon Europe, which provide funding for research, innovation, and disaster recovery. For instance, following the catastrophic floods in Germany and Belgium in 2021, the EU allocated millions in aid to help rebuild communities and improve flood defenses.
The Future of Flood Resilience in Europe
As climate change continues to evolve, the threat of flooding in Europe will only intensify. However, the continent’s collective response demonstrates that, with the right combination of technology, policy, and community engagement, Europe can build greater resilience to this ever-growing challenge.
Looking ahead, there is an urgent need to further integrate climate adaptation strategies into urban planning, strengthen early warning systems, and increase funding for long-term flood mitigation projects. Public-private partnerships will also play an essential role in expanding flood defenses, while fostering greater public awareness and collaboration will ensure that communities remain prepared and proactive.
The journey toward a flood-resilient Europe is far from over, but the steps taken today—across all levels of society—will determine the continent’s ability to confront the rising tide of severe flooding tomorrow.
Conclusion
Europe’s resilience to severe flooding is a testament to its commitment to climate adaptation and innovation. While the challenges posed by rising flood risks are significant, the collective efforts of governments, communities, and scientists are laying the groundwork for a safer, more sustainable future. By continuing to embrace forward-thinking solutions and prioritizing collaboration, Europe can confront the growing flood threat and mitigate its impacts for generations to come.
See more Your Daily Weather